Modifying Business Hosts (Legacy UI)
This topic describes how to use the legacy Production Configuration page to modify business hosts.
For information on performing these tasks with the new UI, see Modifying Business Hosts.
Enabling, Disabling, or Restarting a Business Host
You can either enable, disable, or restart business hosts individually or for a selection of business hosts.
To enable, disable, or restart a single business host, do one of the following:
-
Double-click a host item. InterSystems IRIS displays a dialog box that allows you to enable, disable, or restart the host item depending on the current state of the production and the host item:
-
If the production is running and the host item is enabled, the dialog box gives you the option to disable the host item, restart the host item, or to cancel the request.
-
If the production is not running and the host item is enabled, the dialog box gives you the option to disable the host item or to cancel the request.
-
If the host item is disabled, the dialog box gives you the option to enable the host item or cancel the request.
-
-
Select or clear the Enabled setting (as appropriate) and then click Apply. To restart a host item, first disable it and then enable it.
-
Use the Stop, Start, and Restart buttons on the Action tab. Because the setting controlled by the Enabled check box is a setting stored in the production class definition, you cannot use it to stop, start, or restart a production that you cannot edit, for example because you lack sufficient privileges, or it is marked read-only due to being managed by source control system. The Stop, Start, and Restart buttons on the Action tab perform these actions without modifying the production class definition.
To enable, disable, or restart a selection of business hosts, do the following:
-
Select multiple business hosts in the Production Configuration page by using the Ctrl and Shift keys. The Ctrl key keeps any existing selection and either adds or removes the item from the selection. The Shift key allows you to select a contiguous set of one kind of business hosts—either Business Services, Business Processes, or Business Operations.
-
Once you have selected multiple business hosts, the right panel automatically switches to the Actions tab, which will include Enable, Disable, and Restart buttons.
-
Select the button to enable, disable, or restart the selected business hosts.
You cannot disable a business process with a pool size of 0. The management portal does not allow this action because disabling it would stop all business processes with a pool size of 0, which use the same shared actor queue. If you want to disable only a single business process, you must first set its pool size to 1 or more. After you apply the settings, you can disable it. If you do want to stop all business processes using the shared actor pool, select Production Settings and set the Actor Pool Size to 0. Also see Pool Size and Actor Pool Size.
Changing the Class That a Business Host Uses
To modify a business host so that it is based on a different class:
-
Display the Production Configuration page:
-
Click the business host in the diagram.
-
Click the Actions tab.
-
Click Change Class. This button is visible only when you can edit the business host.
-
Select a new class.
Copying a Business Host
To create a copy of a business host within a given production:
-
Display the Production Configuration page:
-
Click the business host in the diagram.
-
Click the Actions tab.
-
Click Copy. This button is visible only when you can edit the business host.
-
Click Copy to create a copy of the selected business host.
A dialog box prompts you to enter a configuration name.
-
Enter a unique name and click OK.
When first created, the copy has the same host class and settings as the original; only the name is different. Generally your next step is to configure the copy to make it unique. For example:
-
If you have an incoming TCP business service that receives messages from a client application, and you want to receive messages from a similar application on a different application server, you can copy the first TCP service and configure the copy with the other server address.
-
If you have a business process for one message routing interface, and you want a similar one but with alterations for another interface, you can copy the first routing process and configure the copy to route messages between different sets of business services and business operations.
-
If you have an outgoing email business operation that alerts a user, but you want to alert another user at different times of day, you can copy the first outgoing email operation and configure the copy with the other email address.
The copy has no relationship to the original item; you can configure, enable, and disable each item independently.
The Copy command works only within the same production. You cannot copy a business host from one production to another.
Deleting a Business Host
To delete a business host within a given production:
-
Display the Production Configuration page:
-
Click the business host in the diagram.
-
Click the Actions tab.
-
Click Delete. This button is visible only when you can edit the business host.
This process removes this item from the production configuration. This action does not delete the business host class on which the business host is based.
Repairing an Error
If the class for a given business host is not available, the diagram displays the item with a red background. To fix the error:
-
Select the item.
-
Click the Actions tab.
-
Now either click Delete to remove the item or click Change Class to choose a class. This button is visible only when you can edit the business host.
Viewing and Configuring Connections
When you click the status indicator of a business host, lines connect items as defined by the values in the Target Config Names setting or, in the case of a routing process, as defined by the associated Business Rule Name. The following figure shows an example:
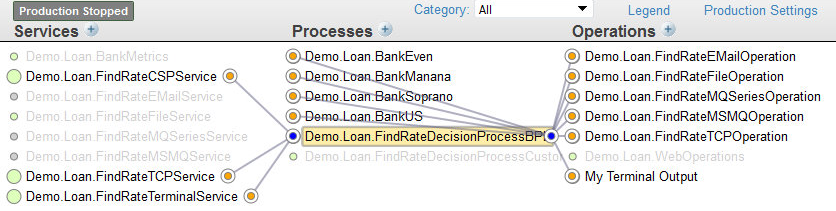
You can assign a business service Target Config Names by clicking its status indicator and dragging the pointer to a business process or operation until you see its status indicator highlighted. When you do so, the Production Configuration page displays a dialog window requesting you to confirm the connection. If you confirm the connection, the page displays a Settings applied message and the item is added to the list in the Target Config Names setting.
Working with Multiple Versions of a Business Host
During development, it can be convenient to include multiple versions of a business host in the production and then switch among them for testing.
Only one of them can be enabled at any time; when you enable one, InterSystems IRIS automatically disables any previously enabled version.
To create and work with multiple versions of a host:
-
Add the first business host as usual.
-
Add the next business host and provide the same configuration name as for the first one.
The production configuration still shows only one business host with the given name.
-
If you are not in listing view, click the listing view icon
 .
. -
Select the business host.
Now the diagram displays a small box that indicates the number of items that have this name, as follows:
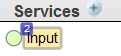
Also, the area above the diagram shows a drop-down list that you can use to select the specific item to work with:
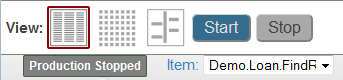
By default, the enabled version is selected. If no host is enabled, the selected version is the first business host that you added.
-
Use the Item list to select the version that you want to configure. Specify configuration details as usual and apply them.
-
Repeat if needed.
To understand why this is useful, consider the following: when testing or troubleshooting the production you might want to send messages by typing them at the console command line, or by reading data from files. But when running the production, you might intend for these messages to arrive from an external application via a TCP connection. Each means of obtaining input for the production requires a different business service host class.