VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT (SQL)
Synopsis
VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT(vec1, vec2)
Description
The VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT function finds the dot product of two input vectors. These vectors must be of a numeric type, either integer, double, or decimal. The result is the value of the dot product, represented as a double, and can be useful when trying to determine the similarity between two vectors.
The dot product of two vectors is the sum of the products of each pair of elements in the same position of the two input vectors. The formula for this calculation is presented below:
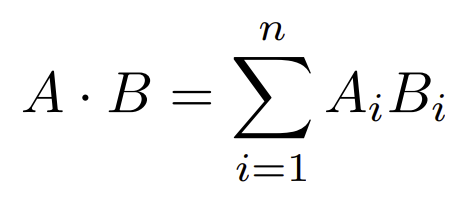
If the input vectors are unit vectors, the dot product is the same value as the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. The larger the dot product, the more similar the vectors are. Taken to the extreme, when the dot product between two unit vectors is 1, they are the same vector; when the dot product between the vectors is -1, then the two vectors are completely different.
InterSystems recommends only using this function on unit vectors (that is, vectors normalized to 1). When this operation is performed on non-unit vectors, the result can rapidly approach the numeric overflow value; in this case, you should instead use VECTOR_COSINE. The following table lists what the overflow (and underflow) values for each valid VECTOR type are:
| Overflow Boundary | Underflow Boundary | |
| Integer | 2,147,483,647 (231-1) | -2,147,483,648 (-231) |
| Double | 1.79769e+308 | 2.22507e-308 |
| Decimal | 1.79769e+308 | 2.22507e-308 |
| Float | 3.402823e+38 | 1.175494e-38 |
InterSystems recommends using this function over VECTOR_COSINE, as the calculation takes advantage of the efficiency of the VECTOR type.
Arguments
vec1, vec2
Two vectors that are both of the same numeric type. If the vectors are of differing numeric types, the function fails with a SQLCODE -259.
If you specify a vector that has a non-numeric type, such as string, the function fails with a SQLCODE -258.
The two vectors must have the same length. If the two vectors have different lengths, the system throws a SQLCODE -257 error.
Examples
The following example uses the VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT function on two integer vectors.
SELECT VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT(TO_VECTOR('6,4,5',integer), TO_VECTOR('1,4,3',integer))
The following example uses the VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT function to return the text descriptions that are most similar to the results based on the similarity between the vector stored in each row and an input vector. In reality, an embedding vector has many more than three elements; however, for the sake of keeping this example brief, the embedding vector is represented as having three elements.
SELECT TOP 5 Description FROM Sample.DescAndEmbedding emb
ORDER BY VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT(Embedding,TO_VECTOR('1,1,1',double)) DESC